[Laplacian]图像求导
OpenCV提供了二阶求导算子Laplacian
Laplacian算子
对于Sobel算子而言,图像边缘区域的像素值变化剧烈,其表现在一阶导数上就是出现极大值
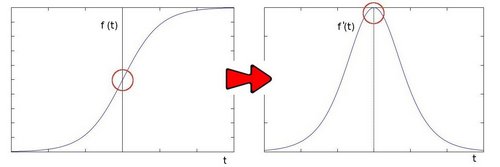
Laplacian算子计算的是图像的二阶导数,此时边缘区域的像素值在二阶导数中表现为0值

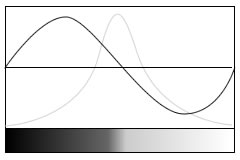
与一阶导数相比,二阶导数能够区分像素值递增和递减区域,并且通过比较递增极大值和递减极小值,能够进一步区分出像素值变化缓慢和剧烈区域
对于二维图像而言,其数学公式如下:
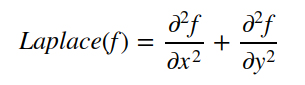
需要对水平和垂直方向进行二阶求导操作
函数解析
参考:Laplacian()
CV_EXPORTS_W void Laplacian( InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int ddepth,
int ksize = 1, double scale = 1, double delta = 0,
int borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT );
src:原图dst:结果图像ddepth:输出图像深度,使用CV_16S以避免溢出dx:导数在x轴方向的阶数dy:导数在y轴方向的阶数ksize:Sobel内核大小,比如3/5/7/9/11等等scale:计算导数值的比例因子,默认为1delta:添加到每个梯度的值,默认为0borderType:边界填充类型,默认为BORDER_DEFAULT
源代码地址:/path/to/modules/imgproc/src/deriv.cpp
if( ksize == 1 || ksize == 3 )
{
float K[2][9] =
{
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, -4, 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 2, 0, 2, 0, -8, 0, 2, 0, 2 }
};
Mat kernel(3, 3, CV_32F, K[ksize == 3]);
if( scale != 1 )
kernel *= scale;
CV_OCL_RUN(_dst.isUMat() && _src.dims() <= 2,
ocl_Laplacian3_8UC1(_src, _dst, ddepth, kernel, delta, borderType));
}
if( ksize == 1 || ksize == 3 )
{
float K[2][9] =
{
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, -4, 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 2, 0, 2, 0, -8, 0, 2, 0, 2 }
};
Mat kernel(3, 3, CV_32F, K[ksize == 3]);
if( scale != 1 )
kernel *= scale;
filter2D( _src, _dst, ddepth, kernel, Point(-1, -1), delta, borderType );
}
else
{
int ktype = std::max(CV_32F, std::max(ddepth, sdepth));
int wdepth = sdepth == CV_8U && ksize <= 5 ? CV_16S : sdepth <= CV_32F ? CV_32F : CV_64F;
int wtype = CV_MAKETYPE(wdepth, cn);
Mat kd, ks;
getSobelKernels( kd, ks, 2, 0, ksize, false, ktype );
...
...
}
当ksize=1时,OpenCV提供的内核为
0 1 0
1 -4 1
0 1 0
通过差分方式进行计算,并没有平滑的效果
当ksize=3时,OpenCV提供的内核为
2 0 2
0 -8 0
2 0 2
示例
#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
#include <iostream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
// 滑动条名
const string ksize_trackbarname = "ksize";
const string scale_trackbarname = "scale";
const string delta_trackbarname = "delta";
// 窗口名
const string winname = "Laplacian Demo - Simple Edge Detector";
// 最大值
const int maxNum = 4;
int ksize_value, scale_value, delta_value;
Mat image, src, src_gray;
int ddepth = CV_16S;
void onLaplacian(int, void *) {
int ksize = 1 + 2 * (ksize_value % 5); // ksize取值为 1/3/5/7/9
double scale = 1 + scale_value; // scale取值为 1/2/3/4/5
double delta = 10 * delta_value; // delta取值为 0/10/20/30/40
Mat grad, abs_grad;
Laplacian(src_gray, grad, ddepth, ksize, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT);
// converting back to CV_8U
convertScaleAbs(grad, abs_grad);
imshow(winname, abs_grad);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
cv::CommandLineParser parser(argc, argv,
"{@input |../lena.jpg|input image}"
"{help h|false|show help message}");
cout << "The sample uses Laplacian OpenCV functions for edge detection\n\n";
parser.printMessage();
String imageName = parser.get<String>("@input");
// As usual we load our source image (src)
image = imread(imageName, IMREAD_COLOR); // Load an image
// Check if image is loaded fine
if (image.empty()) {
printf("Error opening image: %s\n", imageName.c_str());
return 1;
}
// Remove noise by blurring with a Gaussian filter ( kernel size = 3 )
GaussianBlur(image, src, Size(3, 3), 0, 0, BORDER_DEFAULT);
// Convert the image to grayscale
cvtColor(src, src_gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
namedWindow(winname);
createTrackbar(ksize_trackbarname, winname, &ksize_value, maxNum, onLaplacian, NULL);
createTrackbar(scale_trackbarname, winname, &scale_value, maxNum, onLaplacian, NULL);
createTrackbar(delta_trackbarname, winname, &delta_value, maxNum, onLaplacian, NULL);
onLaplacian(0, NULL);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
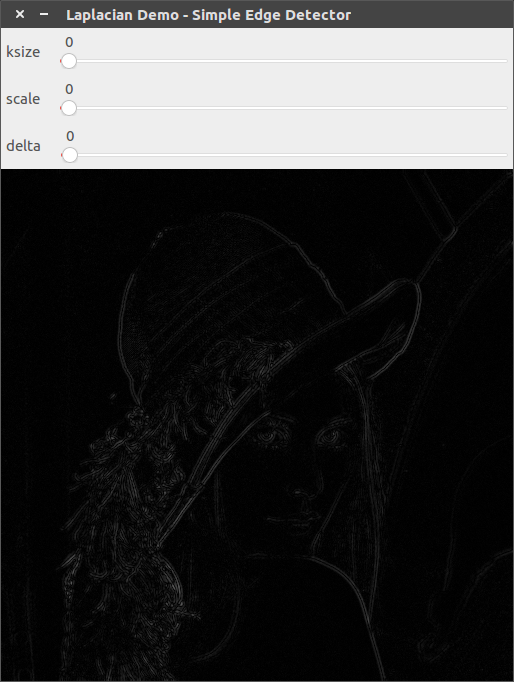
ksize=1, scale=1, delta=0
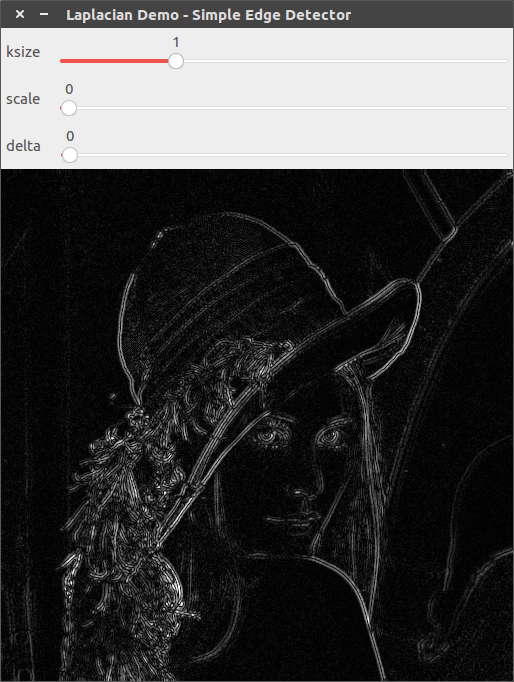
ksize=3, scale=1, delta=0
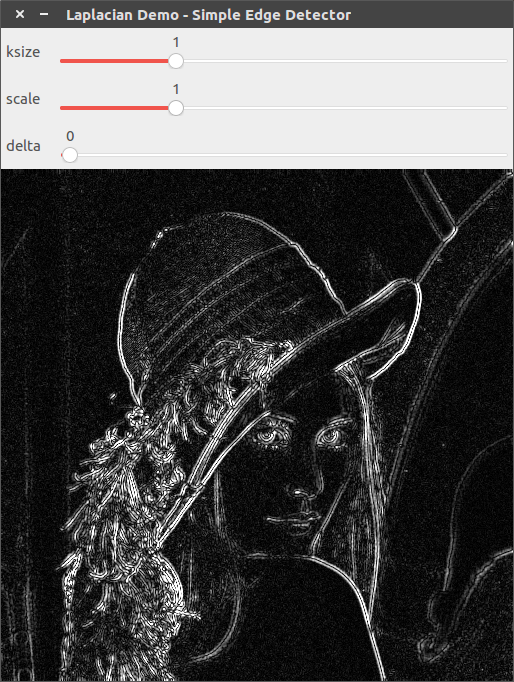
ksize=3, scale=2, delta=0
小结
OpenCV中的Laplacian实现和Sobel/Scharr实现相比,没有高斯平滑功能,更注重像素值的变化,所以能够得到更加精细的图像轮廓