[ElementTree]读取XML文件
很多python模块提供了读取XML文件功能,参考用 ElementTree 在 Python 中解析 XM,利用xml.etree.cElementTree实现XML文件读取(操作最简单易懂,符合tree的读取)
XML文件
XML测试文件如下,表示一个图像的标注数据,包含了被标注的图像信息以及标注信息
<annotation>
<filename>000005.jpg</filename>
<source>
<database>The VOC2007 Database</database>
<annotation>PASCAL VOC2007</annotation>
<image>flickr</image>
<flickrid>325991873</flickrid>
</source>
<size>
<width>500</width>
<height>375</height>
<depth>3</depth>
</size>
<object>
<name>chair</name>
<pose>Rear</pose>
<truncated>0</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>263</xmin>
<ymin>211</ymin>
<xmax>324</xmax>
<ymax>339</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
<object>
<name>chair</name>
<pose>Unspecified</pose>
<truncated>0</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>165</xmin>
<ymin>264</ymin>
<xmax>253</xmax>
<ymax>372</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
<object>
<name>chair</name>
<pose>Unspecified</pose>
<truncated>1</truncated>
<difficult>1</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>5</xmin>
<ymin>244</ymin>
<xmax>67</xmax>
<ymax>374</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
</annotation>
其结构如下图所示
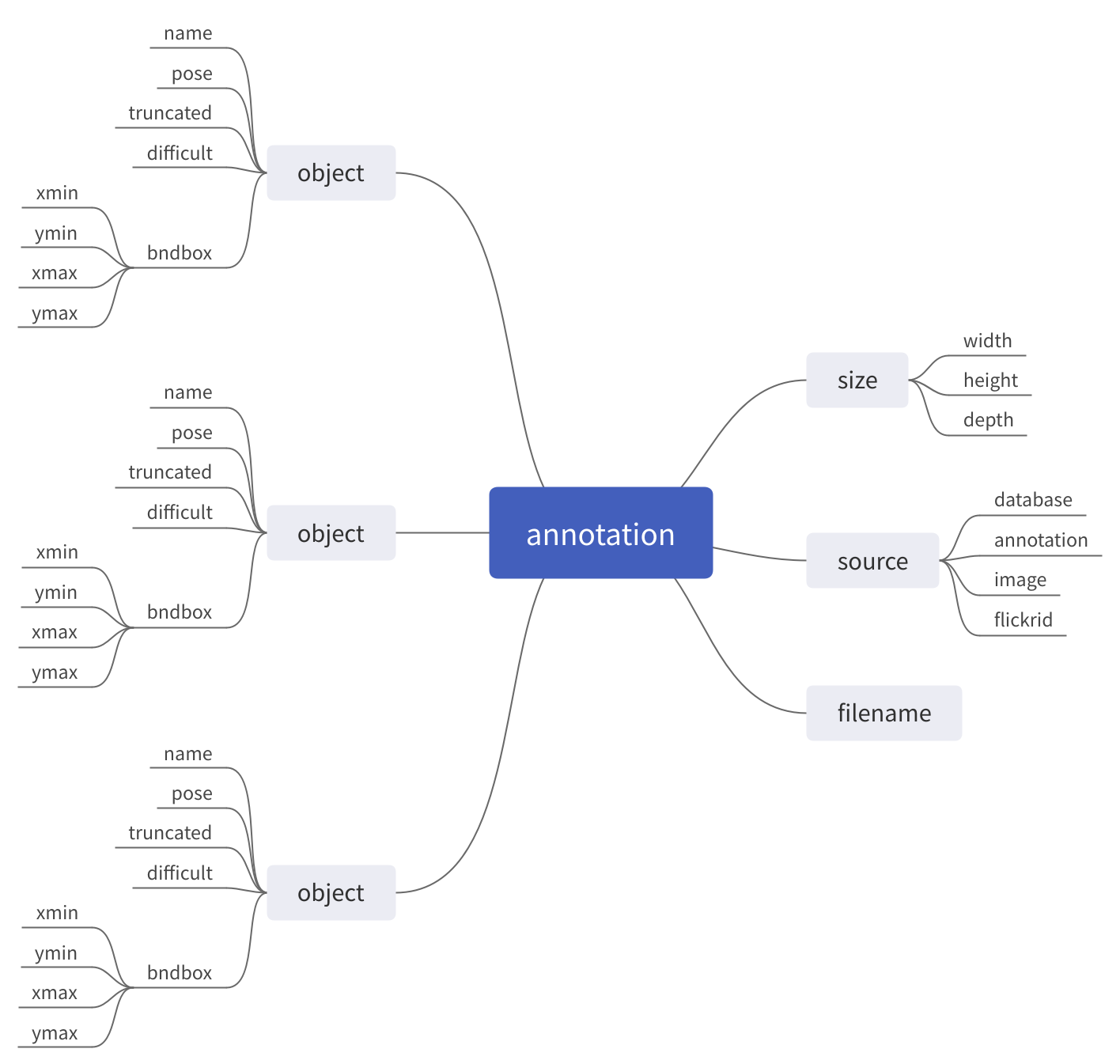
解析
加载解析模块,读取xml文件
import xml.etree.cElementTree as ET
tree = ET.ElementTree(file='xml_test.xml')
读取根节点
root = tree.getroot()
每个节点均包含节点名tag和属性attrib
读取根节点名和属性
print(root.tag, root.attrib)
// 输出
annotation {}
类似数组一样按下标读取子节点
读取所有节点
for child in root:
print(child.tag, child.attrib)
// 输出
filename {}
source {}
size {}
segmented {}
object {}
object {}
object {}
读取size节点
>>> size = root[4]
>>> size
<Element 'size' at 0x7efe63ad0a70>
节点值可通过参数text获取
读取size节点下的子节点widht/height/depth的值
>>> for child in size:
... print(child.tag, child.text)
...
width 500
height 375
depth 3
示例
读取图像名(filename),图像宽/高/深度(width/height/depth),以及标注的目标名(name)和边界框坐标(xmin/ymin/xmax/ymax)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@author: zj
@file: xml.py
@time: 2019-12-07
"""
import xml.etree.cElementTree as ET
if __name__ == '__main__':
tree = ET.ElementTree(file='xml_test.xml')
root = tree.getroot()
node_filename = root[0]
print("文件名:", node_filename.text)
node_size = root[2]
node_width = node_size[0]
node_height = node_size[1]
node_depth = node_size[2]
print('文件大小(宽, 高, 深度):(%s, %s, %s)' % (node_width.text, node_height.text, node_depth.text))
for i in range(3, 6):
node_obj = root[i]
node_name = node_obj[0]
node_bndbox = node_obj[4]
node_xmin = node_bndbox[0]
node_ymin = node_bndbox[1]
node_xmax = node_bndbox[2]
node_ymax = node_bndbox[3]
print('目标:' + node_name.text)
print('边界框坐标:(%s, %s, %s, %s)' % (node_xmin.text, node_ymin.text, node_xmax.text, node_ymax.text))
实现结果如下
文件名: 000005.jpg
文件大小(宽, 高, 深度):(500, 375, 3)
目标:chair
边界框坐标:(263, 211, 324, 339)
目标:chair
边界框坐标:(165, 264, 253, 372)
目标:chair
边界框坐标:(5, 244, 67, 374)